Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Burn Wound Infections
Keywords:
Antibiotics, Burn Wound Infections, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, SusceptibilityAbstract
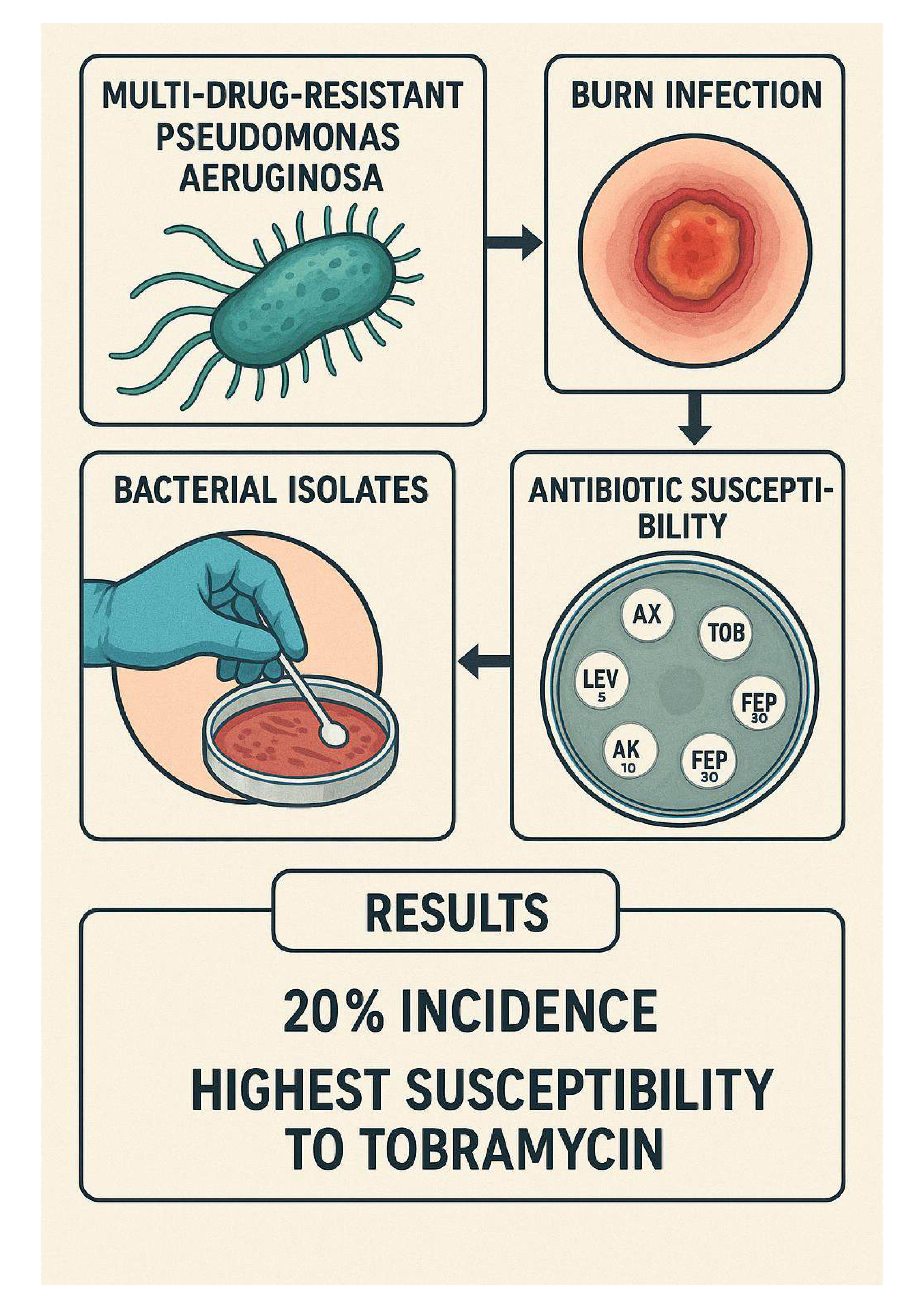
Multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the biggest challenges facing public health. The ability of these bacteria to develop resistance mechanisms makes it essential to routinely monitor their resistance to antibiotics. The current study aimed to investigate the incidence of burn infections caused by P. aeruginosa and to evaluate the susceptibility of these bacterial isolates to several antibiotics commonly used in the treatment of infected wounds. One hundred and fifty swabs were collected from infected burn samples. These swabs were cultured on various differential and selective media. The biochemical tests were used to identify the isolates. The VITIK 2 system was used to confirm the species of isolated bacteria. The Kirby–Bauer method was also used to determine the susceptibility of P. aeruginosa isolates to several antibiotics, including amoxicillin (AX), tobramycin (TOB 10), levofloxacin (LEV5), amikacin (AK10), gentamycin (CN10), and cefepime (FBP10), by measuring the diameters of inhibitory zones. The study revealed that the incidence of infected burn wounds caused by P. aeruginosa was 20%, and all isolates were resistant to amoxicillin. The highest susceptibility rate was to tobramycin, followed by levofloxacin. The number of bacteria sensitive to gentamicin, amikacin, and cefepime was 13, 11, and 11, respectively. It can be concluded from the current study that the incidence of burn infection with P. aeruginosa was 20%, and the highest sensitivity of P. aeruginosa was to tobramycin. Thus, we suggest that tobramycin may be a suitable choice for treating infected burn wounds caused by P. aeruginosa.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



