Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from an infected wound in Iraq
Keywords:
Antibiotics, Klebsiella pneumoniae, MDR, Wound.Abstract
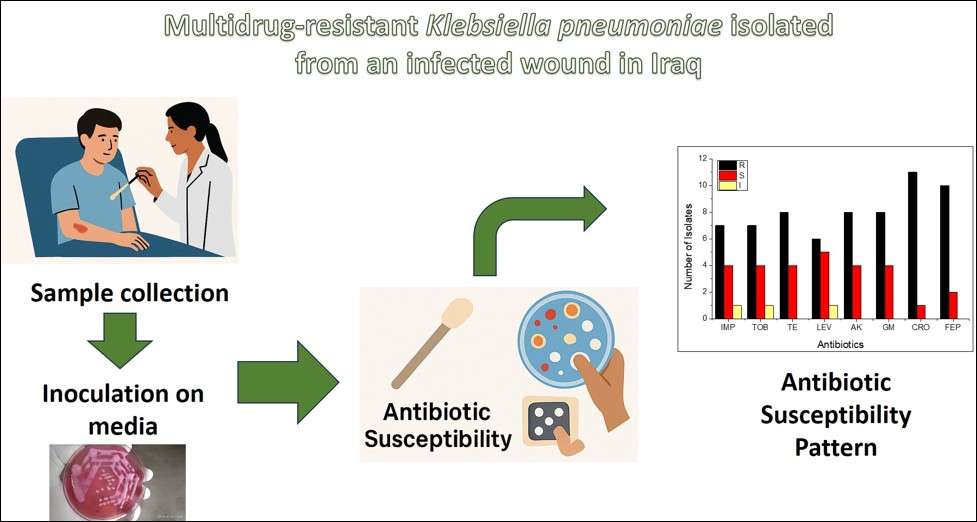
The infected wound with multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria represents one of the big issues for public health. Klebsiella pneumoniae, especially MDR, is responsible for infecting different human organs, particularly wound infections. This current study aims to investigate the antibiotic susceptibility patterns of K. pneumoniae isolates that are responsible for wound infection. In the present study, the samples were collected from Al-Fallujah General Hospital, Al-Anbar, Iraq. A total of 89 wound swabs were collected from patients aged 15 to 65 years, following ethical standards. The microbiological methods were followed for isolation and identification of K. pneumoniae, e.g., culture on selective media, Gram staining, and biochemical tests. The Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion method was used to evaluate susceptibility against eight antibiotics, and results were interpreted using CLSI 2024 guidelines. From 89 wound swabs, 12 isolates of K. pneumoniae were identified, with an infection incidence rate of 13.48%. The antibiotic susceptibility analysis showed a high prevalence of MDR in the isolates. The highest resistance rate was observed against ceftriaxone, followed by cefepime and aminoglycosides (gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin). Imipenem showed high antibacterial efficacy, with four isolates showing susceptibility and one intermediate response. Levofloxacin also showed high effectiveness, with five sensitive isolates. Several isolates exhibited extensive drug resistance, with susceptibility to only one or two antibiotics. The study is highlighting the alarming emergence of MDR K. pneumoniae in wound infections, emphasizing the need for continuous surveillance and rational antibiotic use. Imipenem and levofloxacin remain among the most effective agents that need gene molecular characterization.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All articles in the World Journal of Experimental Biosciences are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.



