Study the Effect of Lemongrass and Rosemary Extracts against Bacterial Pathogens
Keywords:
Antibacterial effect, Lemongrass, Medicinal Plants, Rosmarinus officinalis L.Abstract
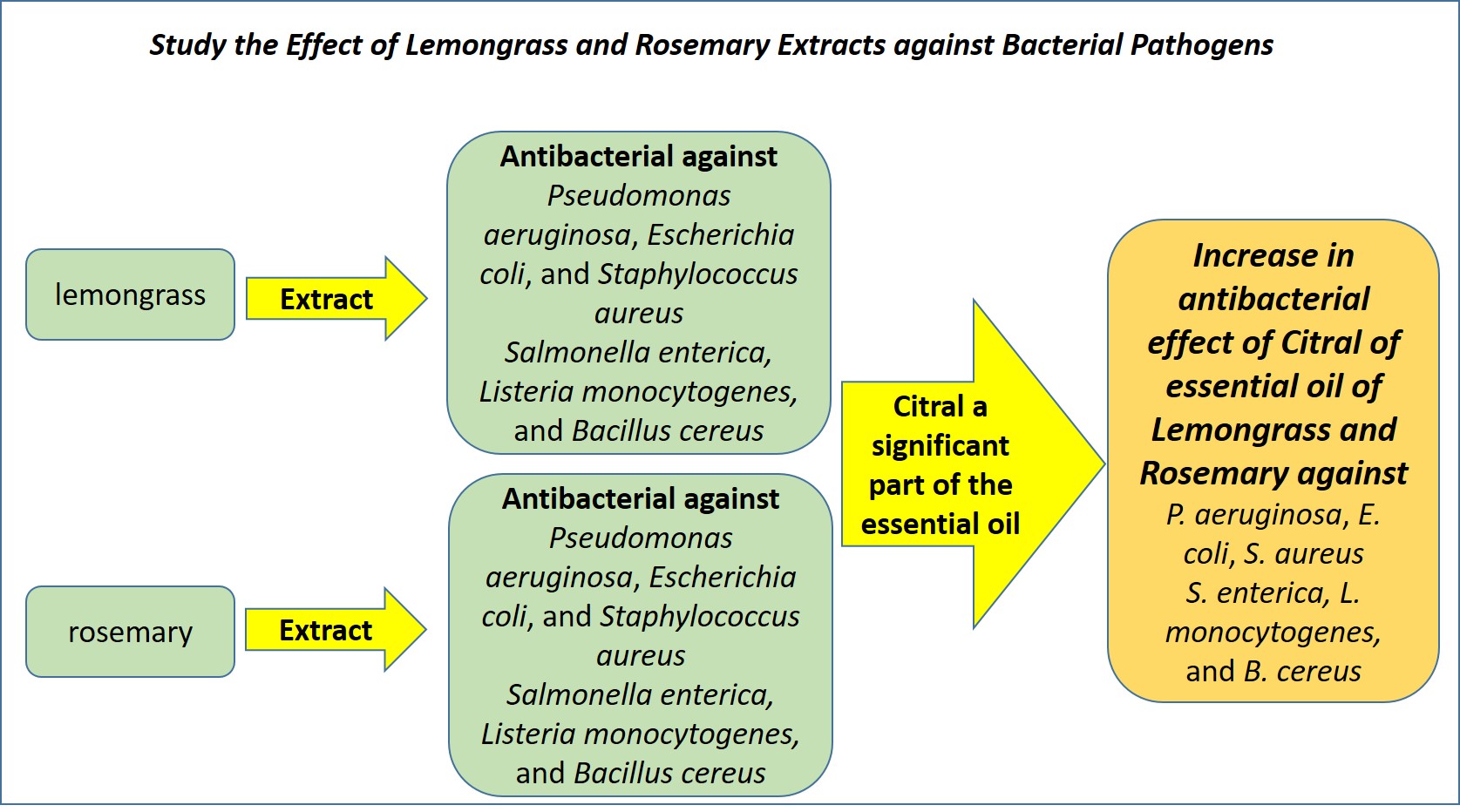
The study aims to study the antibacterial effects of lemongrass and rosemary extracts against different types of bacteria. According to studies, rosemary extract has antibacterial properties against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus. Bioactive substances including rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid are responsible for the antibacterial properties of rosemary extract. Salmonella enterica, Listeria monocytogenes, and Bacillus cereus are just a few of the microorganisms that lemongrass extract has been shown to have antibacterial activity against. Citral a significant part of the essential oil, is the main cause of lemongrass's antibacterial qualities. It has also been discovered that combining the extracts of lemongrass and rosemary has a synergistic effect that increases the antibacterial action against specific bacteria. It is thought that the various modes of action of the bioactive substances included in these extracts are what cause this synergistic impact. All things considered, the data that is now available points to the possibility of using extracts of rosemary and lemongrass as natural antibacterial agents against a range of harmful microorganisms.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All articles in the World Journal of Experimental Biosciences are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.



