Some Toxic Effects of Sio2 NPs on Thyroid Gland Function with Histological Changes and Ovary Function in Female Rats
Keywords:
Estradiol (E2), female rats, T3,T4, TSH,, Histological change, ovary, progesterone, Sio2NPs, thyroid glandAbstract
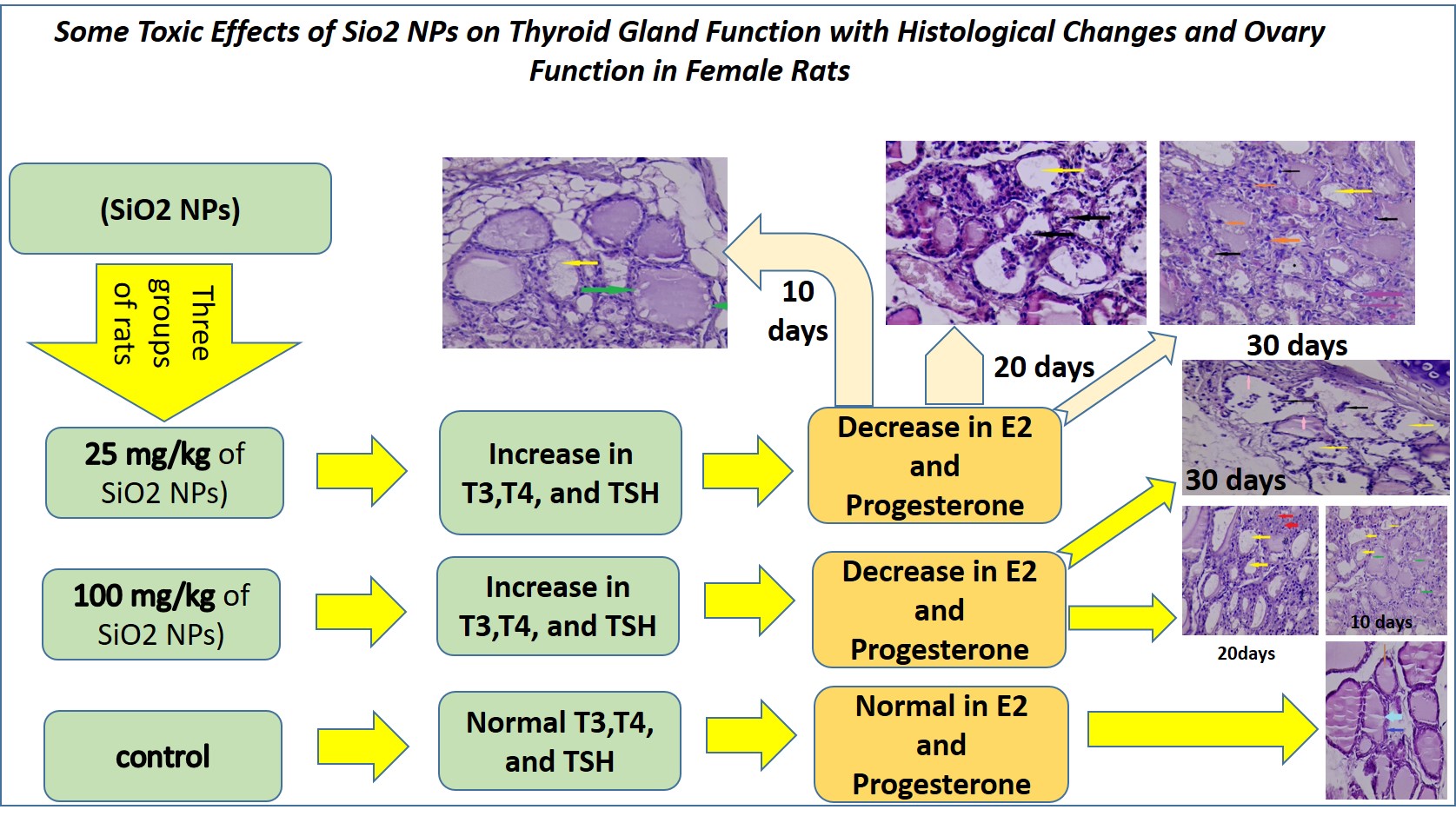
The study investigated the effects of Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs) on female rats' thyroid glands and ovaries. Three groups were randomly selected, and two treatment groups were given different SiO2 NPs (25 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg of body weight). The animals were divided into three experimental groups. The thyroid (T3, T4, and TSH), and ovarian (E2 and progesterone) function hormones were measured. The histological study was studied. It was found that significant decrease in T3 levels in the rats group treated with SiO2 NPs doses over 10 days as compared with the control group. The significant decrease in T4 levels was also found in the treated rats groups (10, 20, and 30 days) as compared with the control group. However, a significant elevation in TSH was seen in treated groups as compared with the control group. The current study showed that exposure to SiO2 NPs caused thyroid tissue alteration, with certain follicles filled with colloidal scalloping activity. When exposed to 100 mg/kg of SiO2 NPs for 10 days, more scalloping formation was observed. When treated with 25 mg/kg of SiO2 NPs for 20 days, few follicles filled with colloidal were observed. When treated with 100 mg/kg of SiO2 NPs for 20 days, empty follicles with necrotic cells were observed. In conclusion, SiO2NPs produced structural, functional, and ovarian effects at different concentrations. In the thyroid gland, they decreased T3 and T4 hormone levels and increased TSH levels. In the ovary, they caused structural, functional, and decreased E2 and progesterone levels.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All articles in the World Journal of Experimental Biosciences are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.



