Antibacterial effect of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil against Ceftazidime-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis
Keywords:
Biofilm, Ceftazidime, Enterococcus faecalis, MDR, Thymus vulgaris essential oil.Abstract
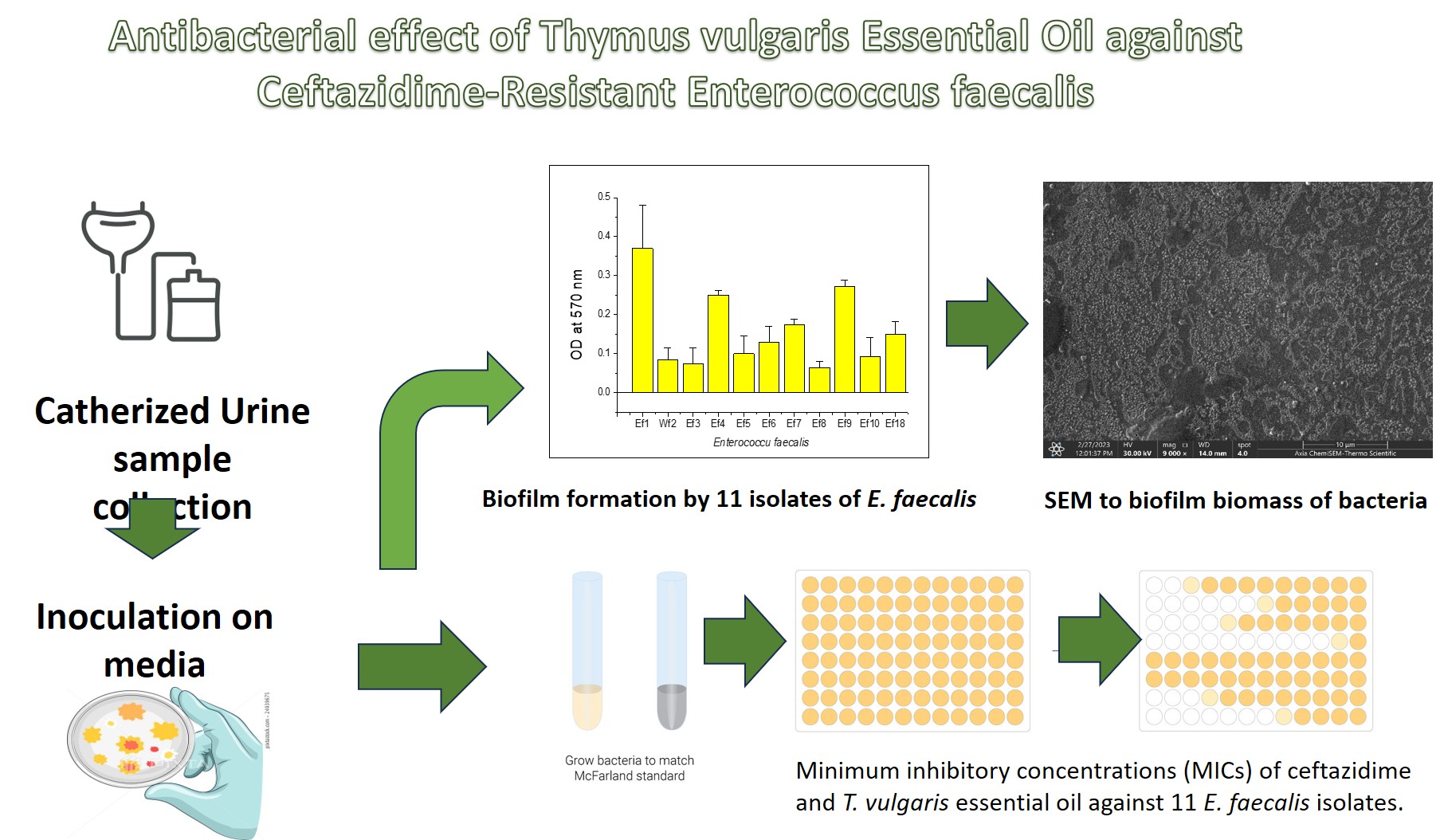
Enterococcus faecalis is an opportunistic pathogen commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. It is associated with biofilm-related infections and increasing resistance to various antibiotics, including cephalosporins. In this study, eleven E. faecalis isolates were obtained from 101 catheter samples collected from patients with severe urinary tract infections (UTIs). All isolates were tested for susceptibility to ceftazidime and Thymus vulgaris essential oil using the microdilution method. Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined using microtiter plates. Biofilm formation was quantified with a crystal violet-based spectrophotometric method. The results showed high-level resistance to ceftazidime (MICs: 1000–4000 µg/mL). Conversely, T. vulgaris essential oil exhibited strong antibacterial activity, with MICs ranging from 1/40 to 1/640 (v/v). All isolates produced biofilms to varying extents, with isolate Ef1 generating the highest biomass. The study confirmed that E. faecalis produces a substantial amount of biofilm and is resistant to ceftazidime. Additionally, the findings highlight the promising antibacterial effects of T. vulgaris essential oil against ceftazidime-resistant E. faecalis.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All articles in the World Journal of Experimental Biosciences are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.



